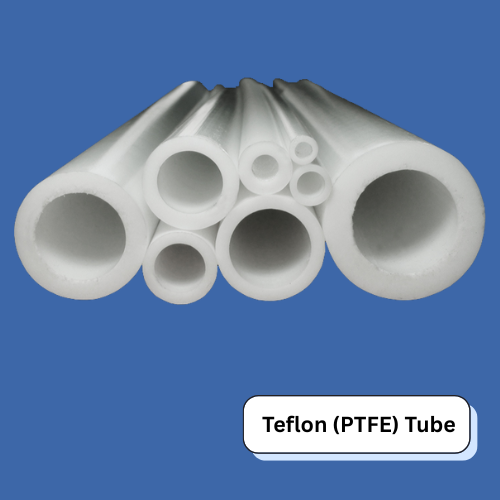
What is a Teflon (PTFE) Tube?
Teflon (PTFE) tubes are engineered for superior chemical resistance, exceptional high-temperature stability, and low-friction performance, making them an ideal solution for demanding industrial applications. Manufactured using premium-grade PTFE, these non-reactive and non-stick tubes are widely used in chemical transfer, fluid transportation, pharmaceutical, electrical insulation, and automotive industries due to their ability to withstand corrosive substances and harsh environments.
Teflon tubes have a hydrophobic surface, high dielectric strength, and robust durability, ensuring optimal safety, reliability, and efficiency in critical systems, while their versatility allows seamless integration into diverse applications.
What are the Features of Teflon (PTFE) Tubes?
These features collectively make Teflon (PTFE) Tube a versatile and reliable choice across various industries that require chemical resistance, thermal stability, and non-stick properties.
- Exceptional Chemical Resistance: Teflon (PTFE) tubes exhibit outstanding resistance to a broad range of chemicals, including strong acids, solvents, and organic compounds, making them ideal for use in corrosive environments within chemical processing and pharmaceutical applications.
- Wide Temperature Range: These tubes operate reliably over a wide temperature range, from approximately −200°C to −260°C (- 328°F to 500°F), making them suitable for both cryogenic and high-temperature industrial applications.
- Low Coefficient of Friction: Teflon (PTFE) Tube has the lowest friction coefficient among polymers, providing a non-stick surface that allows fluids to flow freely with minimal resistance and reduces wear over time.
- Durable and Flexible: The material maintains its strength and structural integrity across a wide range of temperature variations and mechanical stresses, offering excellent impact resistance and flexibility for easy installation.
- Excellent Electrical Insulation: Teflon tubes are an outstanding dielectric material, useful in the electronic and electrical industries for insulation purposes.
- Non-toxic and Biologically Inert: It is safe for use in medical and food-grade applications due to its non-reactive, non-toxic, and FDA-compliant nature.
- Weather and UV Resistant: Teflon tubes resist degradation from UV light, oxygen, ozone, and weathering, ensuring longevity in outdoor and harsh environmental conditions.
- Appearance: Typically translucent to opaque white, indicating purity and quality of the tubing material.
- Self-lubricating: The tubes’ low friction provides self-lubrication, reducing maintenance needs in moving or dynamic applications.
- Wide Industrial Use: Common in aerospace (fuel and hydraulic lines), automotive (chemical-resistant hoses), medical devices, chemical processing, electronics, and 3D printing setups.
Applications
Teflon (PTFE) tubes are valued across a wide range of industries due to their unique properties and adaptability. In the chemical processing industry, these tubes are extensively used for safely transferring corrosive chemicals, acids, and solvents. Their exceptional chemical resistance ensures that the tubing does not react with or contaminate the fluids being handled, making them ideal for laboratory and industrial chemical applications.
In the medical field, Teflon (PTFE) tubes are employed in catheters and guide wires because their smooth, non-stick surface reduces friction, facilitating easier and safer insertion in the body. Their biocompatibility and non-toxic nature also make them suitable for drug delivery systems.
The food and beverage sector relies on PTFE tubing for hygienic fluid transfer due to its non-toxic, non-stick surface that prevents bacterial growth and ensures easy cleaning. PTFE tubes maintain the purity and flavor of food and drinks during processing and dispensing.
In the aerospace and automotive industries, PTFE tubes are utilized in fuel lines, hydraulic systems, and high-temperature environments due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh chemicals. Their low-friction properties improve the performance and durability of mechanical parts.
PTFE tubing also finds applications in electronics as insulation for wiring and components due to its excellent dielectric strength. In 3D printing, PTFE tubes guide filament smoothly between the extruder and hot end, enhancing reliability.
Furthermore, PTFE tubes are utilized in the environmental and energy sectors, including hydraulic systems in wind turbines and solar panel production, which benefit from their UV resistance and weather durability.
Overall, Teflon (PTFE) Tubes offer versatility, safety, and performance in environments demanding chemical inertness, temperature resilience, and biocompatibility.
How to Use?
Before using a Teflon (PTFE) Tube, it is important to understand the proper steps for its effective application. The steps below help ensure safe and effective usage, as well as extend the service life of PTFE Teflon tubes in various industrial and medical applications.
- Identify the specific needs of your application, including chemical compatibility, temperature requirements, and mechanical stresses.
- Choose the correct tube size, wall thickness, and type to match your operational conditions.
- Cut the tubing cleanly to the required length with a sharp cutter to ensure proper fitting.
- Connect the tubing to compatible fittings and hardware, ensuring tight, leak-proof seals.
- Secure the tubing using clamps or supports to prevent movement and reduce wear.
- Conduct pressure and leak tests after installation to confirm system integrity.
- Perform periodic inspections and maintenance to detect wear, cracks, or chemical damage early.
- Follow all safety guidelines appropriate to the industry and application, especially when handling high-temperature or hazardous materials.
Safety Guidelines
Here are the safety guidelines for Teflon (PTFE) Tube:
- Use within recommended temperature limits (below 260°C/500°F).
- Ensure proper ventilation when heating to avoid toxic fumes.
- Handle with gloves to prevent contamination.
- Avoid exposure to open flames or excessive heat.
- Store in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and harsh environments.
- Use protective gear when cutting or installing to prevent injuries.
- Regularly inspect for damage or wear.
- Adhere to pressure and chemical compatibility standards.
- Dispose of waste according to regulations.
- Ensure adequate ventilation during high-temperature processes, such as 3D printing.